Business Intelligence | 29 May 2023 | 10 min
The new paradigm of Business Intelligence

Traditional Business Intelligence (BI) solutions have been improving decision making for industries for quite some time now. This holds true especially with the growth of business analytics, both from the analysis and visualization point of view.
Let us ask an honest question to ourselves: “Is this is enough in today’s business context across industries?” The answer is that it may be helpful, but only to a certain extent.
The traditional enterprise data warehouse can store transactional information captured from multiple systems, including Excel/flat files that have some structure or pattern. An analytical model can be created with or without an OLAP layer to provide rich analytics in terms of dashboards and reports. Mining models can be created and integrated with a data warehouse or OLAP layer to build predictive analytics. At the end, these business analytics tools should help the target audience to find out ‘What’, ‘When’, ‘How’, ‘Where’ and ‘What may (will)’ happen with respect to their business.
The Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) belonging to various industries have built their products and solutions using business intelligence modules to provide better insights of the business processes. However, these business analytics are limited to the information that has been captured through the structured software.
Today, we have greatly evolved in terms of capturing vast amounts of non-transactional, unstructured business data from disparate sources and storing it. This has inevitably paved the way for a new generation of business intelligence tools and such as Power BI. The usage of ‘Hadoop’ as a Big Data platform either in addition to enterprise data warehouse or as substitute has started to rise. The key drivers for this paradigm shift are:
The new technologies help in enhanced data management, new deployment options, and advanced analytics for ISVs to make their software products suitable for today’s business needs. This is the game changer for ISVs. Usually, in the healthcare, retail and e-commerce space, the applications have progressed by leaps and bounds. Here are some top use cases that are applicable for ISVs across industries:
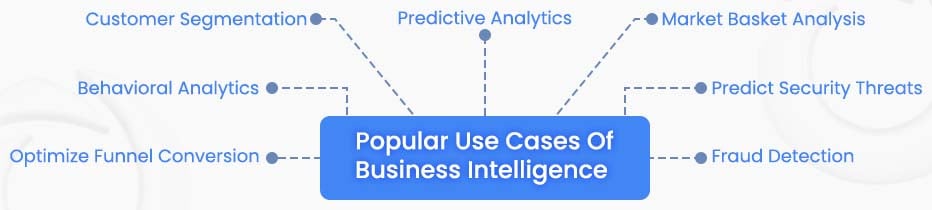
In this new era of social, mobile, analytics and cloud (SMAC), the data is generated through either sensor systems, machines, mobiles, web logs or interactions through social media. This data is unstructured, voluminous, and varied. However, it is critical when combined & analyzed with the structured data captured through traditional systems. Today, after a transformation over the course of time, the new eco system of business intelligence includes two critical components:
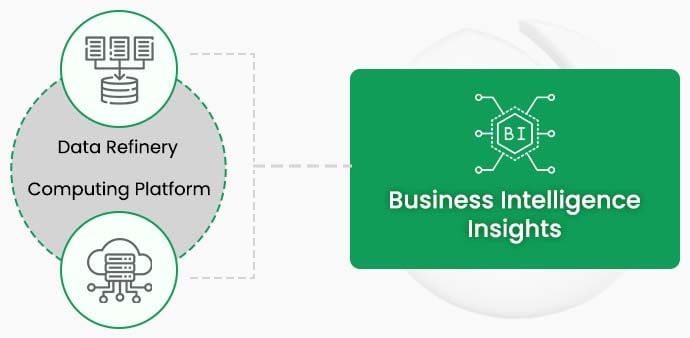
This way the paradigm shift has taken place in business intelligence tools and platforms. Unsurprisingly, it is also creating a dire need for ISVs to modernize and build their software products and applications with above capabilities. The ISVs that have sensed this and have started implementing the change are gaining a competitive advantage.
Business Intelligence analytics tools and BI analytics are ushering in a new age of business. Combined with mobile BI and open-source BI tools, the BI market will surely surge ahead.
The ISVs have already realized the potential of cloud, and moved their software and applications there by offering SaaS based services to the customers. The next big question in their mind is: “Can a Business Intelligence module can be moved there?” This has its own advantages and apparent challenges that can be addressed. This has given rise to ‘AaaS – Analytics As a Service’. Stay tuned for our next blog where we deep dive into this..

we'll keep you in the loop with everything that's trending in the tech world.
