Artificial intelligence | 08 Feb 2023 | 11 min
A Comprehensive Guide to Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Part 1

In today’s modern technology world, every business is curious and talking about OCR. OCR stands for “Optical Character Recognition”. It is a technology that converts an image of typed, handwritten or printed text into a machine-readable text format. OCR software analyzes an image of text and uses one of two algorithms i.e. Pattern Recognition and Feature Recognition to identify and extract the characters. These are then converted into machine-encoded text.
Optical character recognition (OCR) is sometimes referred to as text recognition. OCR systems use a combination of hardware and software to convert scanned images, PDFs, and other documents into editable and searchable text. Hardware such as scanners and software typically handles the advanced processing for OCR.
OCR technology is commonly used to digitize historical documents, books, newspaper archives, and other printed materials. It is also used to automate tasks such as data entry and document search.
In today’s blog, we will dive into the history of OCR and understand how OCR works!
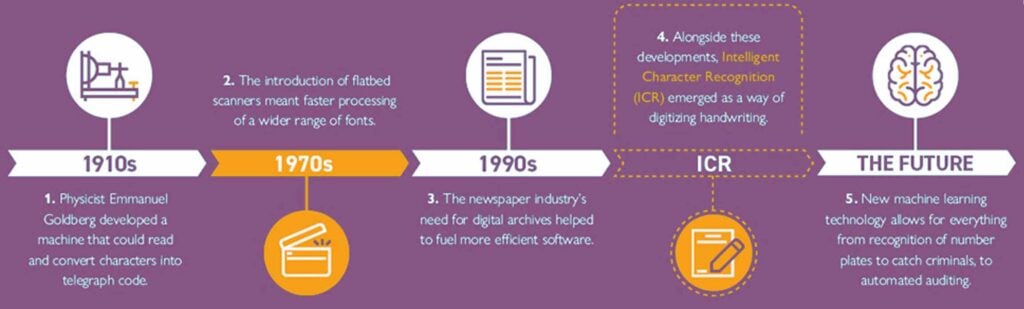
Allow me to first walk you through the history of OCR.
In 1974, Ray Kurzweil started Kurzweil Computer Products, Inc., whose omni-font optical character recognition (OCR) product could recognize text printed in virtually any font. He decided that the best application of this technology would be a machine-learning device for the blind. So he created a reading machine that could read text aloud in a text-to-speech format.
In 1980, Kurzweil sold his company to Xerox, which was interested in further commercializing paper-to-computer text conversion.
This technology became popular in the early 1990s while attempting to digitize historic newspapers. Now you can imagine, since then technology has undergone several drastic improvements. Nowadays it’s capable of recognizing most characters and fonts to a high level of accuracy with the help of Artificial intelligence (AI). This is to implement the more advanced method of Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR).
Source: https://www.crownrms.com
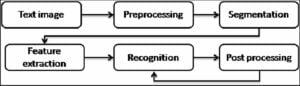
Now we know what OCR is, let’s understand how OCR works behind the scenes.
Here is a general overview of how OCR works:
Source: https://www.researchgate.net
This is the most important process which needs to be done before sending an image for OCR. This process includes different techniques such as the input image being cleaned and prepared for recognition. This may include tasks such as removing noise, de-skewing, and binarizing the image (converting it to black and white called a “binary image”). This helps us for better accuracy.

Source: medium.com

Source: verypdf.com
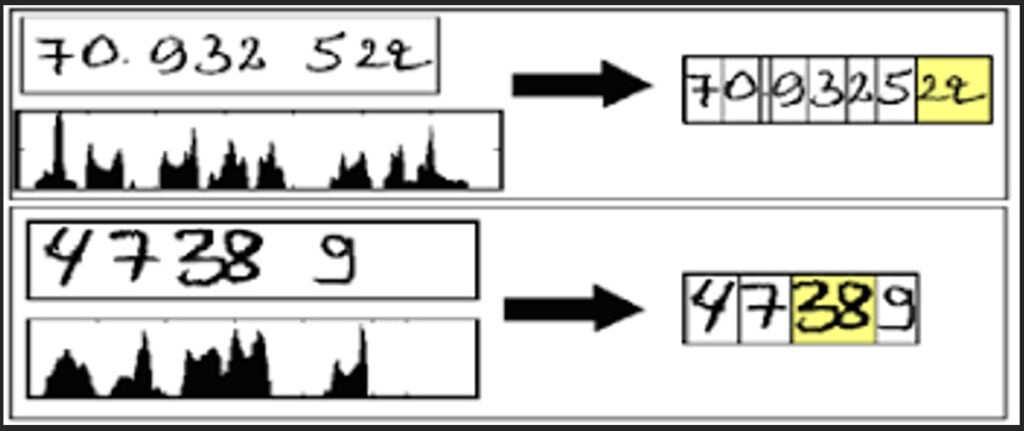
The image is divided into small regions, such as lines, words, and characters.
Source: https://www.researchgate.net
The segments are analyzed to extract features such as shape, size, and texture. These can be used to distinguish one character from another.

Source: https://ijcsit.com
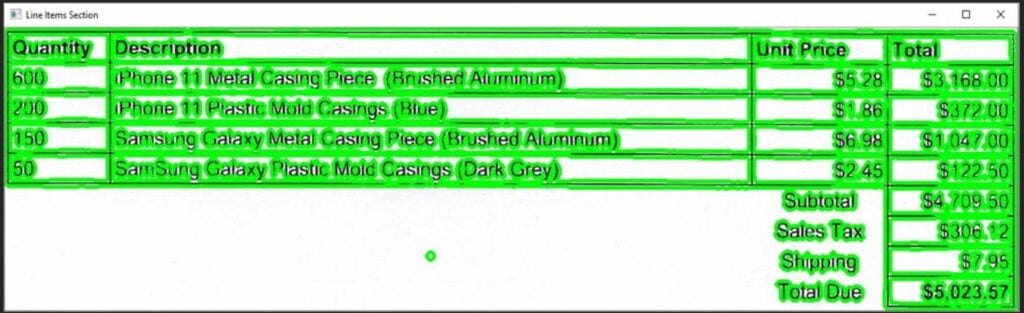
The extracted features are compared to a database of known characters. The system makes a prediction about the text in the image.
Source: https://codetoprosper.com
The recognized text is checked for errors and corrected if necessary. Also in this process, we can extract the required data as per our use case and convert it into JSON or CSV format.
There are many factors on which OCR accuracy depends like the quality of input images. If an image is of low or poor quality, then definitely there are chances of less accuracy. So it is better to have quality images. Some software uses advanced algorithms such as machine learning to train their models. These models are trained on a large dataset of different images.
There are many factors on which OCR accuracy depends like the quality of input images. If an image is of low or poor quality, there are chances of less accuracy. So, it is better to have quality images. Some software uses advanced algorithms such as machine learning to train their models. These models are trained on a large dataset of different images.
Here are a few top OCR software services that industries are using:
Amazon Textract is a service offered by AWS (Amazon Web Services) that uses OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology to automatically extract text and data from scanned documents and images. It can also analyze the document’s structure and extract information such as tables, forms, and key-value pairs. Here there is no need for train models. You can directly input images or PDFs using their different APIs based on the type of your document like receipts and invoices, and identity documents.
Form Recognizer is a service offered by Azure Cognitive Services. This is a collection of artificial intelligence (AI) services and APIs provided by Microsoft. It is a service that uses machine learning to extract text, key-value pairs, tables, and fields from forms and documents.
Form Recognizer uses a pre-built or pre-trained machine learning model. It can analyze the structure of a document and identify different types of fields such as names, addresses, and dates. Users can also train custom models specific to their needs and use them to extract fields from their documents.
It is a service offered by Google Cloud Platform that uses machine learning to analyze and understand images. It includes a number of features such as OCR, object detection, and image labeling.
The OCR feature of Google Cloud Vision allows for the extraction of text from images and documents. It can recognize text in a wide range of languages and scripts, including handwriting and cursive text. The service can also extract information from structured documents such as invoices and receipts.
It is an open-source OCR engine developed by Google. It uses machine learning algorithms to recognize text in images and can handle a wide range of languages and scripts.
Tesseract can recognize text in images of various formats such as PNG, JPG, and TIFF, and can also handle image pre-processing tasks such as image thresholding and deskewing.
Tesseract is a command-line tool and can be integrated with other software to provide OCR functionality. It’s widely used in many OCR projects and is considered one of the most accurate open-source OCR engines.

Next, in part 2 of my blog, delve into the benefits of OCR, present and future use cases of OCR, as well as possible alternatives to OCR.
Meanwhile, write to us with your thoughts about this blog. Visit us at Nitor Infotech to learn more about our cognitive engineering offerings!

we'll keep you in the loop with everything that's trending in the tech world.
